

During this activity, students should be able to:
This activity helps students develop the following skills, values and attitudes: proficiency in English, ability to analyze and synthesize, capacity to identify and solve problems, and efficient use of computer systems.
Individually or in pairs, solve the following set of problems using Python 3.5. Run and test each of your programs to make sure they work as expected.
Each source file must include at the top the authors’ personal information (student ID and name) within comments. For example:
# Authors: # A01166611 Pepper Pots # A01160611 Anthony Stark # # Description of problem being solved. # # March 30, 2017. . . (The rest of the program goes here) .
Write a program called positives.py. Define in this program a function called positives(x) that takes a list of numbers x as its argument, and returns a new list that only contains the positive numbers of x.
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(positives([-21, -31])) print(positives([-48, -2, 0, -47, 45])) print(positives([-9, -38, 49, -49, 32, 6, 4, 26, -8, 45])) print(positives([-27, 48, 13, 5, 27, 5, -48, -42, -35, 49, -41, -24, 11, 29, 33, -8, 45, -44, 12, 46])) print(positives([-2, 0, 27, 47, -13, -23, 8, -28, 23, 7, -29, -24, -30, -6, -21, -17, -35, -8, -30, -7, -48, -18, -2, 1, -1, 18, 35, -32, -42, -5, 46, 8, 0, -31, -23, -47, -4, 37, -5, -45, -17, -5, -29, -35, -2, 40, 9, 25, -11, -32]))
The expected program output should be:
[] [0, 45] [49, 32, 6, 4, 26, 45] [48, 13, 5, 27, 5, 49, 11, 29, 33, 45, 12, 46] [0, 27, 47, 8, 23, 7, 1, 18, 35, 46, 8, 0, 37, 40, 9, 25]
Write a program called dotproduct.py. Define in this program a function called dotproduct(a, b) that takes two arguments: the lists a and b. It returns the result of performing the dot product of a times b. The dot product is an algebraic operation that takes two equal-length sequences of numbers and returns a single number obtained by multiplying corresponding entries and then summing those products:
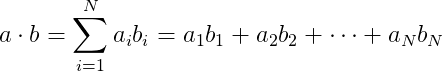
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(dotproduct([], [])) print(dotproduct([1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6])) print(dotproduct([1.3, 3.4, 5.7, 9.5, 10.4], [-4.5, 3.0, 1.5, 0.9, 0.0])) print(dotproduct([92, -39, 82, 16, -64, -1, -16, -45, -7, 39, 45, 0, 34, -3, -51, 71, 23, -8, 41, -40], [-50, -81, 94, -84, 47, 86, 52, 19, -57, 36, -20, 11, -42, 48, 14, 13, 9, -67, 92, 96]))
The expected program output should be:
0 32 21.45 357
Write a program called replicate.py. Define in this program a function called replicate(n, x) that takes two arguments: a list x and an integer number n, where n ≥ 0. It returns a new list that replicates n times each element contained in x.
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(replicate(7, [])) print(replicate(0, ['a', 'b', 'c'])) print(replicate(3, ['a'])) print(replicate(3, ['a', 'b', 'c'])) print(replicate(4, [1, 2, 3, 4]))
The expected program output should be:
[] [] ['a', 'a', 'a'] ['a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'b', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'c'] [1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 4, 4, 4]
The Fibonacci sequence is:
0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, ...
The sequence starts with 0 and 1. Any number that follows is calculated by adding the previous two numbers.
Write a program calledfibo.py. Define in this program a function called fibo(n) that returns a list with the first n Fibonacci numbers.
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(fibo(0)) print(fibo(1)) print(fibo(2)) print(fibo(5)) print(fibo(10)) print(fibo(20)) print(fibo(30)) print(fibo(100))
The expected program output should be:
[] [0] [0, 1] [0, 1, 1, 2, 3] [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34] [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181] [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765, 10946, 17711, 28657, 46368, 75025, 121393, 196418, 317811, 514229] [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55, 89, 144, 233, 377, 610, 987, 1597, 2584, 4181, 6765, 10946, 17711, 28657, 46368, 75025, 121393, 196418, 317811, 514229, 832040, 1346269, 2178309, 3524578, 5702887, 9227465, 14930352, 24157817, 39088169, 63245986, 102334155, 165580141, 267914296, 433494437, 701408733, 1134903170, 1836311903, 2971215073, 4807526976, 7778742049, 12586269025, 20365011074, 32951280099, 53316291173, 86267571272, 139583862445, 225851433717, 365435296162, 591286729879, 956722026041, 1548008755920, 2504730781961, 4052739537881, 6557470319842, 10610209857723, 17167680177565, 27777890035288, 44945570212853, 72723460248141, 117669030460994, 190392490709135, 308061521170129, 498454011879264, 806515533049393, 1304969544928657, 2111485077978050, 3416454622906707, 5527939700884757, 8944394323791464, 14472334024676221, 23416728348467685, 37889062373143906, 61305790721611591, 99194853094755497, 160500643816367088, 259695496911122585, 420196140727489673, 679891637638612258, 1100087778366101931, 1779979416004714189, 2880067194370816120, 4660046610375530309, 7540113804746346429, 12200160415121876738, 19740274219868223167, 31940434634990099905, 51680708854858323072, 83621143489848422977, 135301852344706746049, 218922995834555169026]
In statistics, the standard deviation σ is a measure of how spread out numbers are. It has the following formula:
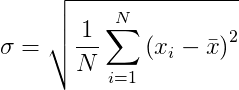
Where x is the arithmetic mean and is defined as follows:
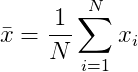 Write a program called
Write a program called deviation.py. Define in this program a function called deviation(x) that returns the standard deviation of the list of numbers contained in x.
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(deviation([42])) print(deviation([10, 20])) print(deviation([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])) print(deviation([7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7, 7])) print(deviation([32, 88, 20, 26, 14, 24, 26, 44, 14, 94, 94, 72, 8, 46, 92, 50, 38, 56, 60, 84]))
The expected program output should be:
0.0 5.0 1.4142135623730951 0.0 28.673855687716646
Write a program called compress.py. Define in this program a function called compress(x) that takes a list x as its argument. If x contains consecutive repeated elements, they should be replaced with a single copy of that element. The order of the elements should not be changed.
Test your program with the following main() function:
def main(): print(compress(['a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'b', 'c', 'c', 'a', 'a', 'd', 'e', 'e', 'e', 'e'])) print(compress(['a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a', 'a'])) print(compress(['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'])) print(compress([]))
The expected program output should be:
['a', 'b', 'c', 'a', 'd', 'e'] ['a'] ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd'] []
Create a ZIP file called lists.zip containing only the six programs you wrote (positives.py, dotproduct.py, replicate.py, fibo.py, deviation.py, and compress.py.
To deliver the lists.zip file, please provide the following information:
If this activity was developed by a team of two people, only one person is required to deliver it. No activity will be accepted through e-mail or any other means.
Due date is Thursday, March 30.
This activity will be evaluated using the following criteria:
| -10 | One or more programs don’t contain within comments the authors’ personal information. |
|---|---|
| DA | One or more programs were plagiarized. |
| 10-100 | Depending on the amount of problems that were solved correctly. |